Bayesian Force Field Optimization
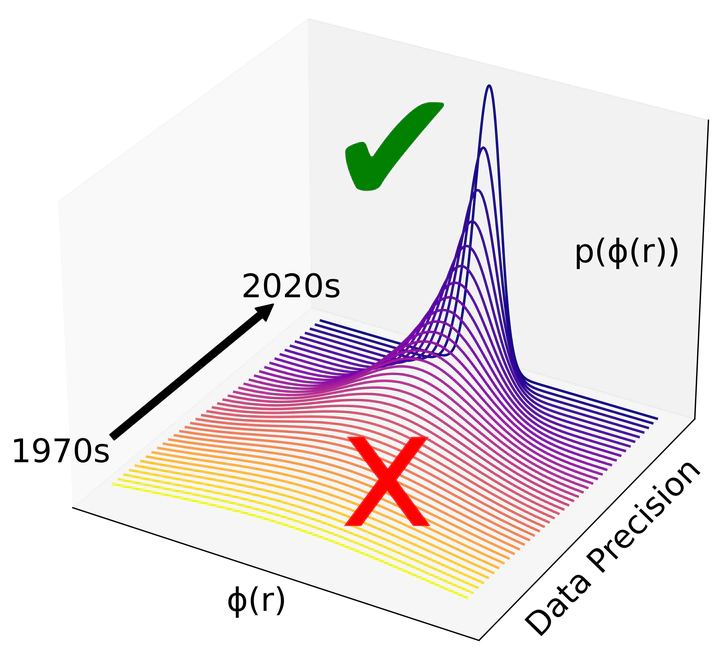
Structure and self-assembly are complex, emergent properties of matter that are often misrepresented by existing molecular simulation models. In this project, we use Bayesian optimization, an accurate and robust statistical method, to optimize novel force fields based on experimental neutron/X-ray diffraction data to better model the structural behavior of liquid state systems.
We have developed an efficient and simple method to implement Bayesian inference for molecular simulations using local Gaussian process surrogate models [1] and are currently working on specific applications of Bayesian inference in neutron scattering. For instance, we have shown that neutron scattering data must be very precisely measured in order to directly learn interatomic forces [2], demonstrating for the first time that it is possible to learn subtle features of the interaction potential such as repulsive exponent and dispersion energy.
[1] B.L. Shanks, H.W. Sullivan, A. R. Shazed and M.P. Hoepfner, Accelerated Bayesian Inference for Molecular Simulations using Local Gaussian Process Surrogate Models, J. Chem. Theory Comput. (2024), https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.3c01358
[2] B.L. Shanks, H.W. Sullivan, M.P. Hoepfner. Bayesian Analysis Reveals the Key to Extracting Pair Potentials from Neutron Scattering Data. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. (2024), https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c02941#